 Many of us look in the mirror and notice that around some or all of our teeth the gums are disappearing. In many cases, the teeth involved are sensitive to hot or cold and often the appearance of the teeth is longer than what we would like. The questions we are most often asked related to this issue are: “Does this need to be treated?” and “Can it be treated?” In order to answer these questions, we must first review what is considered healthy.
Many of us look in the mirror and notice that around some or all of our teeth the gums are disappearing. In many cases, the teeth involved are sensitive to hot or cold and often the appearance of the teeth is longer than what we would like. The questions we are most often asked related to this issue are: “Does this need to be treated?” and “Can it be treated?” In order to answer these questions, we must first review what is considered healthy.
Healthy Gums:
A tooth consists of both the crown (the part we see in the mouth) and the root (the part under the gum and in the bone supporting the tooth). Typically, jaw bone surrounds the root. This bone is covered by gum tissue. To be clear, if we look in our mouths, we can see the crown of the tooth only. Below the crown we see gum tissue which is covering the bone.
It is also important to understand that we have 2 different type of gum tissue in our mouths, thick and thin. Thick tissue is the dense tissue on the roof of our mouths, while thin tissue is the soft, stretchy tissue inside our cheeks. The difference is important as the thick, dense tissue helps protect and prevent gum loss. Our teeth are surrounded by both types of this gum tissue. The thick tissue is usually present right where the gum and crown meet.
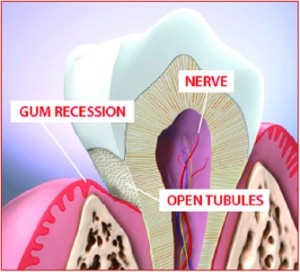
What Happens:
Many different factors can lead to gum recession (loss). Common examples include poor oral hygiene, smoking, medical issues such as diabetes, overly aggressive brushing and misaligned teeth. As the gum starts to recede, we first lose thick gum until it eventually reaches the thin gum which recedes at an even quicker rate. When the gum tissue goes away it leaves the underlying bone exposed. This causes the jaw bone to resorb away as well.
Problems:
As you can imagine, losing gum and bone around our teeth can lead to a number of problems. First of all, if we lose jaw bone eventually the teeth themselves will become loose and ultimately be lost. Secondly, as the gum and jaw bone recede, the root part of the tooth becomes exposed to the mouth. The root does not have a protective layer of enamel on it like the crown does, which can allow cavities to occur at a more rapid rate. Root cavities often lead to tooth problems at a quicker rate than traditional cavities. Other issues related to recession involve sensitivity to hot and cold, along with a less pleasing appearance (longer looking teeth).
What Can Be Done:
The main goal of treatment of this type of periodontal problem is to slow or stop the progression of the recession. There is no true cure to this problem and it is something a patient will deal with for their entire life. Research has shown that gum procedures have a high success rate of slowing down the gum and bone loss. Typically, treatment options involve developing a new band of thick tissue to put the brakes on the recession. Some situations allow for the gum tissue to be brought back to its original position. Each case needs to be evaluated both clinically in the mouth and with a current set of x-rays in order for your periodontist to determine what treatment option would be best.
Lee R. Cohen, D.D.S., M.S., M.S.
4520 Donald Ross Road, Suite 110
Palm Beach Gardens, FL 33418
Phone: 561-691-0020
www.pbcperio.com
Check Also
RejuvaNATION MedSpa: Elevating Men’s Health to New Heights
Embark on a Journey to Revitalize Your Vitality Rediscover the joy of a spontaneous sex …
 South Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles
South Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles




