By Alan J. Bauman, M.D. –
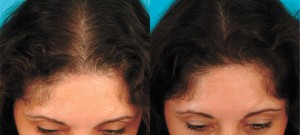
The problem, however, is that if left untreated, gradual female hair loss can result in a significant loss of coverage at the frontal area, crown or temples.
A number of medical conditions and other factor can affect your hair so it’s important to determine all of your risk-factors to be sure you are receiving proper treatment and ruling out more sinister problems. If you’re worried about hair loss, it is important to consult with both your primary doctor and an experienced Hair Restoration Physician—someone who specializes exclusively in the medical diagnosis, treatment and tracking of hair loss and its treatment.
Hair loss before, during or after menopause—as well as after childbirth—is commonly attributed to hormonal changes. And while most physicians agree that replacing these hormones can alleviate many of the other troubling symptoms of menopause, unfortunately, hormone replacement alone does not seem to radically alter a woman’s “follicular fate,” and can even sometimes make matters worse.
No It Wasn’t Your Prenatal Vitamins!
Just as high levels of female hormones during pregnancy leave women with fuller, healthier hair, the declining levels during menopause may have the opposite impact. In addition, when the levels of female hormones fall, the effects of androgens (male hormones) can increase, causing certain hair follicles to fail. Depending on your genetic risks, these follicles produce progressively weaker hair and then eventually none at all. If your doctor has recommended replacing your declining testosterone levels, this also may work against your luscious locks as many aging women can experience increased hair loss from testosterone, especially if they are ‘androgen sensitive.’ Stay tuned for more on that below!
When it comes to menopausal hair loss, lower female hormones might be the most common culprit, but other contributing factors may need to be considered as well. These risk factors include genetic predisposition, unusual levels of stress, other hormonal imbalances—like thyroid, for example—nutritional or iron deficiencies, crash diets, as well as illness, medications, and your surgical history. A detailed medical history and diagnostic tests are obtained as an important part of a medical hair loss evaluation to identify risk factors.
Best-Bets For Female Hair Loss Diagnosis, Treatment & Tracking
Medical treatments that may help mitigate hair loss include the compounded prescription minoxidil solution called Formula 82M, platelet-rich plasma injections (PRP, also called the Vampire hair growth treatment), Latisse (Bimatoprost) or other prostaglandin analogs, low-level laser therapy with the LaserCap, off-label finasteride (for post-menopausal women only) and nutritional supplements like Viviscal Professional and pharmaceutical grade biotin. The best strategy is to use a multi-therapy approach, as prescribed by a hair loss specialist, and routine follow-ups for tracking purposes to see what’s working.
Another tool that has become useful in treating hair loss in menopausal patients is the Androgen-Sensitivity Genetic Hair Loss Test. This test can help predict whether a post-menopausal patient is likely to respond to off-label anti-androgen therapies like finasteride, dutasteride or spironolactone.
Hair Transplants are for Women, too!
In severe cases of female hair loss or in cases where the hairline or temples are affected, hair transplantation can be used to redistribute more permanent living and growing hair follicles from the back of the scalp into those areas to undetectably improve density, artistically restore a natural hairline or enhance scalp coverage. New microsurgical no-scalpel/no-stitch harvesting techniques like NeoGraft FUE or Follicular Unit Extraction allow for a minimally-invasive “follicle-by-follicle” approach. This advanced process allows for diminished downtime and discomfort while avoiding the pluggy look and linear scars which traditional ‘old-style’ hair transplants left behind.
Avoiding the Most Common Treatment Mistakes
The most common mistakes women (and men, for that matter) make when they are trying to treat their hair loss is not giving enough time for therapy to work and not tracking their results properly. Just like hair loss, initial changes in hair regrowth take time and can be subtle before they are noticeable to the naked eye. Scientific diagnostic and tracking methods like HairCam™ scalp microscopy and routine HairCheck™ measurements can help you and your hair restoration physician determine what treatments are working and what areas are improving.
Hair Loss Has Deep Rooted Effects
While hair loss is often falsely thought of as merely a cosmetic problem, studies have proven that hair loss can have wide-ranging psychological effects on women, including loss of confidence and self-esteem, and in some cases, depression, anxiety, social withdrawal and more. Whether your hair loss is the result of natural hormonal changes and/or other underlying causes, in most cases hair loss is a treatable condition and not something you have to live with or hide. Preventing further hair loss and improving hair growth can restore a feeling of vitality, youth and confidence for women.
To learn more about any of these hair regrowth treatments, or to discuss any menopause-related hair loss concerns, contact a Hair Restoration Physician who can work with you to determine the most effective treatment regimen for your specific needs. Patients
should look for a doctor who is a full-time medical hair loss specialist who is certified by the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery and recommended by the American Hair Loss Association. Only a qualified and experienced hair restoration physician can perform natural-looking hair transplants and prescribe the most effective multi-therapy treatment options, including the latest available products.
Key takeaways for women at risk for hair loss:
1. A woman’s chance of losing hair after menopause is almost just as high as it is for men at that age, but female pattern hair loss looks different.
2. It’s easy to miss the early warning signs of female pattern hair loss – but catching it early is key, as 50% loss can occur before it’s noticeable to the human eye. There are a number of effective treatments for female hair loss, but the best results occur when they’re started early on.
3. Hair loss around menopause is common due to changes in hormone levels and activity, but it cannot be commonly cured with hormone replacement alone.
4. Genetic predisposition, unusual levels of stress, hormonal imbalances, vitamin deficiencies, crash diets, medications, as well as a history of illness and surgery can also be contributing factors to female hair loss.
5. Most women benefit from a combination of pharmaceutical and lifestyle changes in treating their hair loss and thinning. Results are proportional to your level of discipline and compliance with the prescribed regimen.
6. Medical treatments to protect and enhance hair follicle functioning may include compounded topical minoxidil Formula 82M, platelet-rich plasma injections, Latisse/Bimatoprost or other prostaglandin analogs, low-level laser therapy, off-label anti-androgens (for post-menopausal women only) and nutritional supplements like Viviscal Professional and pharmaceutical grade biotin.
7. Routine diagnostic and tracking methods with scientific HairCam™ microscopic scalp analysis and HairCheck™ measurements are key to help you and your doctor determine how well your treatments are working and when to make changes to your regimen.
8. No-scalpel/No-stitch hair transplant harvesting techniques like NeoGraft FUE can restore density in severely depleted areas of scalp without the risks of scarring, discomfort, downtime and unnaturalness of old-style procedures.
BAUMAN MEDICAL GROUP
Hair Restauration Men and Women
www.baumanmedical.com
 South Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles
South Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles