By Lauren R. Rosecan, M.D., Ph.D., F.A.C.S. –
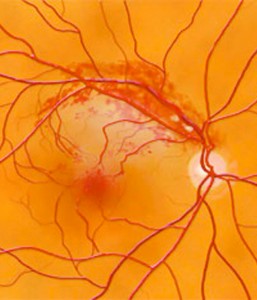 The retina—the layer of light-sensitive cells at the back of the eye—is nourished by the flow of blood, which provides nutrients and oxygen that nerve cells need. When there is a blockage in the veins into the retina, retinal vein occlusion may occur.
The retina—the layer of light-sensitive cells at the back of the eye—is nourished by the flow of blood, which provides nutrients and oxygen that nerve cells need. When there is a blockage in the veins into the retina, retinal vein occlusion may occur.
Branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) is a blockage of the small veins in the retina. (When there is blockage of the main vein in the retina, it is called Central Retinal Vein Occlusion.)
BRVO often occurs when retinal arteries that have been thickened by atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) cross over and place pressure on a retinal vein. When the vein is blocked, nerve cells within the eye may die.
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) Symptoms
Because the macula—the part of the retina responsible for central vision—is affected by blocked veins, some central vision is lost.
The most common symptom of BRVO is vision loss or blurring in part or all of one eye. The vision loss or blurring is painless and may happen suddenly or become worse over several hours or days. Sometimes there is a sudden and complete loss of vision. BRVO almost always happens only in one eye.
Who Is At Risk for Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)?
BRVO is associated with aging and is usually diagnosed in people who are aged 50 and older. High blood pressure is commonly associated with BRVO.
In addition, people with diabetes are at increased risk for BRVO. About 10 percent to 12 percent of the people who have BRVO also have glaucoma. People with atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) are also more likely to develop BRVO.
The same measures used to prevent coronary artery disease may reduce your risk for BRVO. These include:
• eating a low-fat diet;
• getting regular exercise;
• maintaining an ideal weight; and
• not smoking.
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) Diagnosis
If you experience sudden vision loss, you should contact your ophthalmologist immediately. He or she will conduct a thorough examination to determine if you have branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO).
Your ophthalmologist will dilate your eyes with dilating eye drops, which will allow him or her to examine more thoroughly the retina for signs of damage. Among the other tests that your Eye M.D. may conduct are:
• Fluorescein angiography. This is a diagnostic procedure that uses a special camera to take a series of photographs of the retina after a small amount of yellow dye (fluorescein) is injected into a vein in your arm. The photographs of fluorescein dye traveling throughout the retinal vessels show how many blood vessels are closed.
• Intraocular pressure.
• Pupil reflex response.
• Retinal photography.
• Slit-lamp examination.
• Testing of side vision (visual field examination).
• Visual acuity, to determine how well you can read an eye chart.
In addition, you may be tested to determine your blood sugar and cholesterol levels. People under the age of 40 with BRVO may be tested to look for a problem with clotting or blood thickening.
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) Treatment
Because there is no cure for branch retinal vein occlusion, the main goal of treatment is to stabilize vision by sealing off leaking blood vessels. Treatments may include laser treatment and injections.
Finding out what caused the blockage is the first step in treatment. Your Eye M.D. may recommend a period of observation following your diagnosis. During the course of BRVO, many patients will have swelling in the central macular area. This swelling, called macular edema, can last more than one year.
MicroPulse Focal laser treatment can be used to reduce swelling of the macula. With this form of laser surgery, your Eye M.D. applies many non-scarring laser burns to areas of fluid leakage around the macula. The main goal of treatment is to stabilize vision by sealing off leaking blood vessels that interfere with the proper function of the macula. Treatment with injections of Avastin or Eylea in the eye may also be done.
Lauren R. Rosecan
M.D., Ph.D., F.A.C.S.
The Retina Institute of Florida with four offices conveniently located in Palm Beach and Martin Counties.
Toll Free Phone Number: 1-800-445-8898 Or 561-832-4411
West Palm Beach
901 North Flagler Drive, 33401
(561) 832-4411 Office
(561) 832-1591 Fax
Stuart
618 East Ocean Blvd., #3, 34994
(772) 287-7026 Office
(772) 220-4186 Fax
Palm Beach Gardens
11382 Prosperity Farms Rd., #128, 33410
(561) 627-7311 Office
(561) 627-6791 Fax
Boca Raton
1050 NW 15th Street, #114, 33486
(561) 368-7723 Office
(561) 368-0093 Fax
Check Also
Trusted Homecare Agency: Serving Veterans with Free Supplemental Home Healthcare
When it comes to healthcare, veterans deserve the best care possible. For veterans seeking in-home …
 South Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles
South Florida Health and Wellness Magazine Health and Wellness Articles




